[German]A quick reminder that Microsoft is getting serious about hardening Windows clients and servers for the Kerberos protocol as early as February 2025. Microsoft has also introduced a string length limit to the Kerberos policy for host names. Here is a reminder of the timelines for phased hardening and string length limitation in the Kerberos host-to-realm policy, which was introduced in February 2025.
[German]A quick reminder that Microsoft is getting serious about hardening Windows clients and servers for the Kerberos protocol as early as February 2025. Microsoft has also introduced a string length limit to the Kerberos policy for host names. Here is a reminder of the timelines for phased hardening and string length limitation in the Kerberos host-to-realm policy, which was introduced in February 2025.
I have reported several times here on the blog about the relevant hardening measures for Windows clients and servers. In January 2025, my colleagues at deskmodder.de wrote about Windows 10, 11, Server Windows hardening and important dates at a glance (see Windows 10, 11, Server Windows-Absicherung und wichtige Termine im Überblick). And at the end of January 2025, I came across the following post.
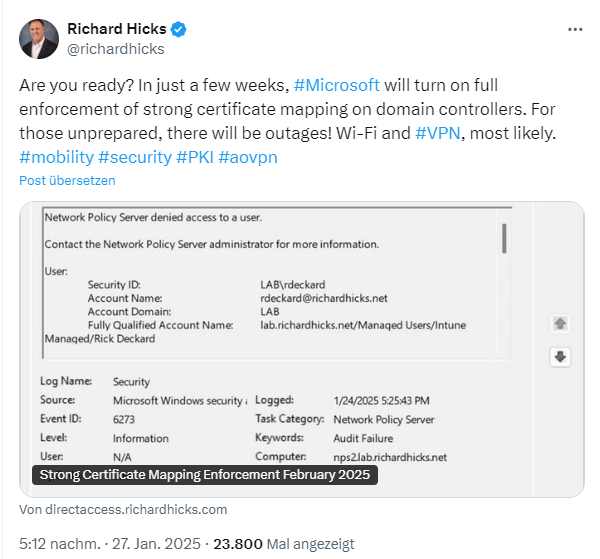
Richard Hicks pointed out that Microsoft will turn on full enforcement of strong certificate mapping on domain controllers from February 2025. Systems that are not prepared for this are likely to show failures. Hicks suspects that there could be trouble in the area of Wi-Fi and VPN. He has published the article Strong Certificate Mapping Enforcement February 2025. The February 2025 patch day is now over and the enforcement measures should be over.
Windows hardening timeline
As of February 19, 2025, Microsoft has now updated its support article Latest Windows hardening guidance and key dates (the changes are editorial in nature), which is why I am revisiting the topic as a reminder. Here are the dates for 2025 and beyond.
- January 2025: PAC Validation changes (KB5037754), Enforcement by default-Phase. Updates for January 2025 and after will put all Windows domain controllers and clients in the respective environment into enforced mode (enforcement mode). In this mode, secure behavior is enforced by default. Existing registry key settings that were previously set will override this change in default behavior. The default settings for enforced mode can be overridden by an administrator to revert to compatibility mode.
- February 2025: With the updates from February 2025 (see KB5014754) and thereafter, phase 3 will be activated for certificate-based authentication (full enforcement mode). If a certificate cannot be uniquely assigned, authentication will be denied.
- April 2025: PAC Validation Changes KB5037754 (Enforcement Phase). The Windows security updates released on or after April 2025 will remove support for the PacSignatureValidationLevel and CrossDomainFilteringLevel registry subkeys and enforce the new security behavior. After installing the April 2025 update, there will no longer be support for compatibility mode.
If you are still using Windows XP systems in an AD environment, you should read the comments in my German article Kerberos PAC-Schwachstellen: Kommt das Ende für Windows XP im April 2025?.
From January 2026, there will be further changes to Secure Boot Bypass protection (KB5025885) and the enforcement phase will begin. Microsoft intends to update the article at least six months before the start of the enforcement phase. The updates for the enforcement phase will include the following:
The "Windows Production PCA 2011" certificate is automatically revoked by adding it to the Secure Boot UEFI Forbidden List (DBX) on capable devices. These updates are enforced programmatically on all affected systems after Windows updates are installed, with no option to disable them.
This presumably also answers the question of what happens if the Windows UEFI CA 2023 certificate is not installed on the affected machines. Details can be found in the linked Microsoft support articles.
Limited string length for Kerberos policy for host names
Microsoft has published the support article Kerberos realm to host mapping policy string-length limitations (KB5054215) on February 20, 2025 (via). The host-to-realm policy in Kerberos is used to map a host (e.g. a client computer or server) to a specific Kerberos realm (see Policy CSP – ADMX_Kerberos). Now Microsoft has introduced string length restrictions in the host-to-realm policy for Kerberos with the February 2025 update.
- User Interface (UI) Character limit for host names: The Group Policy Editor control used to enter the data will not load more than 1,024 characters into the realm host file list entry. However, users can enter up to 32,767 characters and successfully write them to registry.pol.
- Character limit for Host Names: The Kerberos client reading this setting on the device to which the policy applies has a hard limit of 2,048 characters for the hostname list.
The string length limits apply to an Active Directory domain and a third-party realm such as FreeBSD or Linux with an MIT trust. And they become relevant when environments support multiple SPN suffixes or a list of hosts that are manually mapped to the realm that trusts the AD forest. Microsoft describes measures to work around problems with these string length restrictions in the support article.
Similar articles
BlackLotus UEFI bootkit bypasses Secure Boot in Windows 11
KB5025885: Secure boot hardening against vulnerability CVE-2023-24932 (Black Lotus)
Attention: Microsoft's UEFI certificate expires on Oct. 19, 2026 – Secure Boot affected