[German]Does anyone from my readers use the Okta authentication service? Once again there is a security report about this provider. Okta has just closed a login vulnerability that allowed users to log in to certain accounts with any password since July 2024. However, I suspect that the vulnerability was not exploited due to numerous conditions.
[German]Does anyone from my readers use the Okta authentication service? Once again there is a security report about this provider. Okta has just closed a login vulnerability that allowed users to log in to certain accounts with any password since July 2024. However, I suspect that the vulnerability was not exploited due to numerous conditions.
Who is Okta?
Okta is a provider of authentication services (identity and access management in the cloud) that is used by many companies. The company is based in the USA and offers cloud software that helps companies to manage and secure user authentication in applications. The software enables developers to integrate identity controls into applications, website web services and devices. Okta sells six services, including a single sign-on service that allows users to log in to a variety of systems through a centralized process.
The company also offers API authentication services – whereby Okto is based on Amazon Web Services (AWS). Okta has come to my attention in recent years due to the Lapsus$ hack and stolen credentials. If someone cracks Okta's authentication, they have access to the cloud services of the customers in question. This has been a gateway for hacks in recent years.
Authentication vulnerability closed
Okto has closed a vulnerability in the user login to its service on October 30, 2024, which allowed the use of any password for usernames with more than 52 characters.
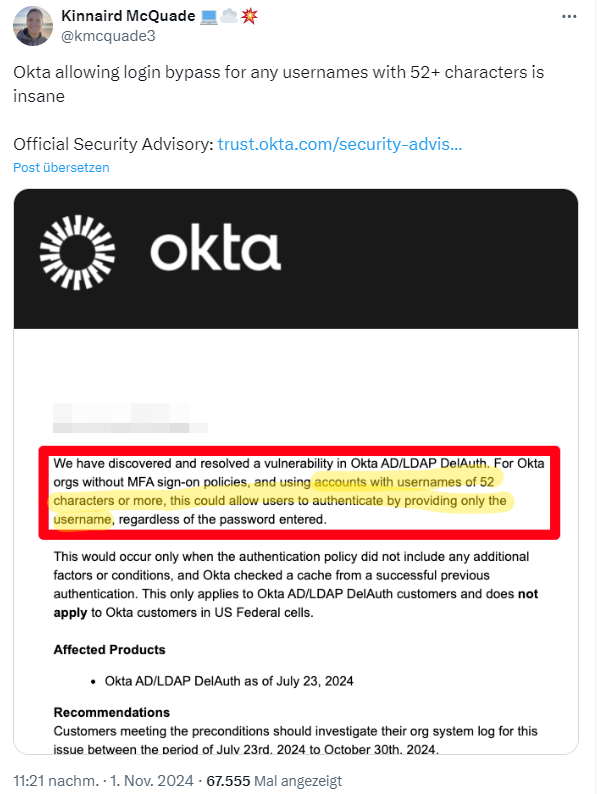
I came across this issue via the above tweet, which was acknowledged by Okta in the Security Advisory Okta AD/LDAP Delegated Authentication – Username Above 52 Characters Security Advisory dated October 30, 2024.
The security advisory states that an internal vulnerability in the generation of the cache key for AD/LDAP DelAuth was identified on October 30, 2024. The Bcrypt algorithm was used to generate the cache key. This algorithm hashes a combined string of userId + username + password.
Under certain conditions, this could allow users to authenticate by providing only the username with the stored cache key from a previous successful authentication. A requirement for this vulnerability is that the username must be at least 52 characters long when generating a cache key for the user.
The Okta AD/LDAP DelAuth product has been affected since July 23, 2024, but according to Okto, the vulnerability can only be exploited if the agent is out of service and cannot be reached – or if there is high traffic. This leads to DelAuth hitting the cache first.
However, due to the numerous restrictions (name longer than 52 characters, agent out of service or high data traffic, availability of a cache key), exploitability is unlikely to have been possible. Customers who meet the requirements should check their login and access control protocols in the period from 23 July 2024 to 30 October 2024 for this problem and any unauthorized access.
Similar articles:
Authentication service OKTA hacked by Lapsus$?
Lapsus$ hacks: statements from Okta and Microsoft
Okta admits a mistake regarding disclosure in "Lapsus$ hack"
Okta support system hacked with stolen credentials
Okta support hack also affects 1Password account